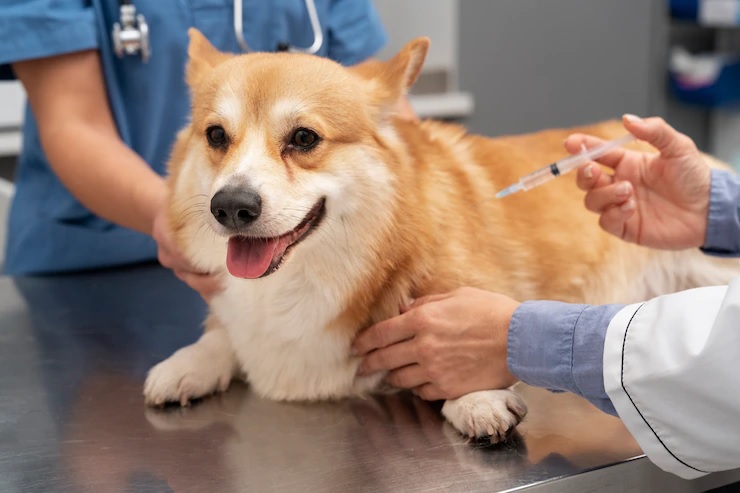
Vaccinations are a vital aspect of pet care, safeguarding our furry companions against a variety of preventable diseases. Just as with humans, vaccines prepare the immune system to combat specific pathogens, ensuring that our pets remain healthy and vibrant throughout their lives. Understanding the significance of pet vaccinations, their types, and recommended schedules can help you make informed decisions for your beloved animals. Here’s a comprehensive overview.
The Importance of Vaccinations
Vaccines play a crucial role in protecting pets from serious and potentially fatal diseases. Many illnesses that affect pets are highly contagious and can spread rapidly within communities. By vaccinating your pets, you not only protect them but also contribute to the broader health of the pet population. Herd immunity is a vital concept here; when a significant portion of the pet population is vaccinated, it creates a protective barrier that reduces the likelihood of disease outbreaks.
Core vs. Non-Core Vaccines
Vaccines are categorized into two primary groups: core and non-core. Core vaccines are those recommended for all pets, regardless of their lifestyle. These vaccines protect against diseases that are widespread and pose significant health risks.
Core Vaccines for Dogs:
- Rabies: A fatal viral disease that affects the nervous system and is transmissible to humans.
- Distemper: A serious viral infection that affects the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and nervous systems.
- Parvovirus: A highly contagious virus causing severe gastrointestinal illness, particularly in puppies.
- Adenovirus: This virus causes infectious hepatitis and can also lead to respiratory illness.
Core Vaccines for Cats:
- Rabies: Similar to dogs, rabies is a critical vaccine for cats.
- Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis (FVR): A leading cause of upper respiratory infections in cats.
- Calicivirus: Another major cause of respiratory illness that can also affect oral health.
- Panleukopenia: A highly contagious viral disease that affects a cat’s immune system.
Non-core vaccines are tailored to specific pets based on their lifestyle, geographic location, and risk of exposure. For instance, pets that frequently interact with other animals or spend time outdoors may require additional vaccinations, such as Bordetella (kennel cough) or Lyme disease vaccines.
Vaccination Schedule
Creating a vaccination schedule is essential for maintaining your pet’s health. Puppies and kittens typically start their vaccination series at around six to eight weeks of age. These initial vaccinations are often followed by boosters every three to four weeks until they reach about 16 weeks old. After this initial series, core vaccines are usually administered on a schedule determined by your veterinarian, often every one to three years, depending on the vaccine type.
For adult pets, it’s crucial to maintain regular veterinary check-ups to ensure they stay up to date on their vaccinations. Your veterinarian will recommend the best schedule based on your pet’s individual health needs and lifestyle.
Potential Side Effects
While vaccines are generally safe, some pets may experience mild side effects. These can include temporary soreness at the injection site, low-grade fever, or decreased energy levels. These reactions typically resolve within a day or two. However, in rare cases, pets can have more severe reactions, such as allergic responses. Signs of a serious reaction may include swelling, difficulty breathing, vomiting, or seizures. If any of these symptoms occur, seek veterinary care immediately.
The Role of Your Veterinarian
Your veterinarian is an invaluable resource when it comes to understanding vaccinations for your pet. They can help tailor a vaccination plan that meets your pet’s specific health needs and lifestyle. Discussing your pet’s environment, behavior, and any potential exposure to infectious diseases will help your veterinarian make informed recommendations.
Additionally, during your visits, your vet will assess your pet’s overall health, ensuring that they are fit for vaccination. If a pet is unwell or has certain medical conditions, vaccination may need to be postponed or adjusted.
Staying Informed
As pet owners, it is essential to stay informed about the latest developments in veterinary medicine and vaccinations. New vaccines and recommendations may emerge, so keeping an open line of communication with your veterinarian is vital. Additionally, reputable veterinary organizations, such as the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) and the World Small Animal Veterinary Association (WSAVA), provide valuable resources for pet owners seeking to understand vaccinations better.
The Bigger Picture
Understanding pet vaccinations is not just about protecting your pet; it also involves considering the health of the broader animal community. By ensuring your pet is up to date on vaccinations, you contribute to a healthier environment for all pets and their owners.
Vaccinations are a cornerstone of responsible pet ownership. They protect your pets from harmful diseases and ensure that your beloved companions can lead long, healthy lives. By working closely with your veterinarian and adhering to recommended vaccination schedules, you are taking proactive steps to safeguard your pet’s health and well-being.